Frameworks
Running SOL in a framework is the easiest operation mode, as SOL takes care of most parameters, options, etc. automatically. In principle you just need to load SOL and run the sol.optimize(model, *inputs, batch_size=None, copy_parameters=True, **named_inputs) function on your target model.
See subchapters for details on the different frameworks and example codes.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| model | Your model you want to optimize using SOL. |
| inputs | Either a list of framework tensors or list of sol.input([sizes], sol.dtype.[...], requires_grad=False). |
| named_inputs | Identical to inputs, but can be key=sol.input(...) |
| batch_size | Heuristic value used, when the inputs contain variable batch sizes. |
| copy_parameters | Determines if the parameters of the original model shall be copied to the optimized SOL model. |
| autotuning | Activates autotuning (default=False) |
Generic Model Functions
SOL models are implemented using the framework’s own model structure, so they provide the same functionality as the framework’s models, except that SOL models always assume, that training = False for inference and training = True for training runs. Additionally they support following functions:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
model.network() |
return the hash of the network |
model.unload() |
Identical to sol.unload(model) |
model.sol_training(bool) |
Only in TensorFlow. This is a bugfix used to tell the model if it is in prediction of training mode. |
model.convert(device=None) |
Converts the memory layout of the parameters into the framework’s native layout. |
model.profiler.get(sol.Pass.[FwdInference, FwdTraining, BwdTraining]) |
Returns a dict with performance stats about the network. |
model.profiler.clear() |
Clears performance stats for this network. |
model.profiler.print() |
Prints performance stats for this network. |
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
sol.config["..."] = ... |
Sets config options |
sol.config.print() |
Prints all config options and their current values |
sol.optimize(...) |
Details here |
sol.deploy(...) |
Details here |
sol.unload(network=None) |
Unloads all or a specific network from the runtime. Network needs to be either a Sol model, or its hash. |
sol.cache.clear() |
Clears Sol’s build cache, to enforce rebuild of models. |
sol.device.enable(device) |
Enables code generation for the specified device. By default all available devices will be build. Device needs to be sol.device.[X86, CUDA, VE] |
sol.device.disable(device) |
See sol.device.enable(device) |
sol.device.set(device, deviceIdx) |
Forces Sol to run everything on the given device. If the data is not located on the target device, it will be explicitly copied between the host and the device. |
sol.profiler.print(network=None) |
Prints performance stats |
sol.profiler.get(network=None, p=None) |
Returns a dict of performance stats for a given network. With default parameters it returns stats of SOL’s internals. |
sol.profiler.clear(network=None) |
Clears performance stats for a given network |
sol.__version__ |
SOL version string |
sol.versions() |
Prints versions of used compiler and libraries. 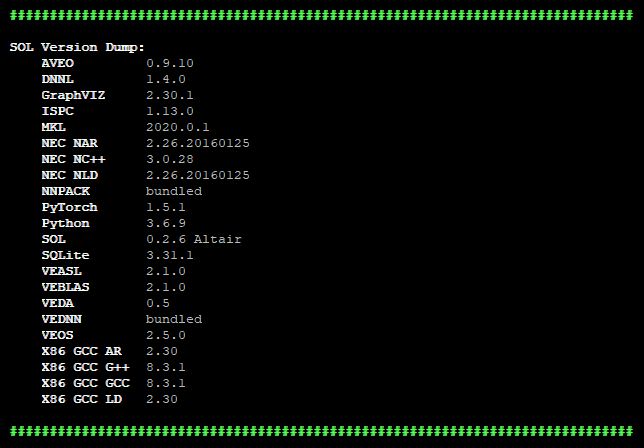 |
sol.devices() |
Prints overview of available devices. 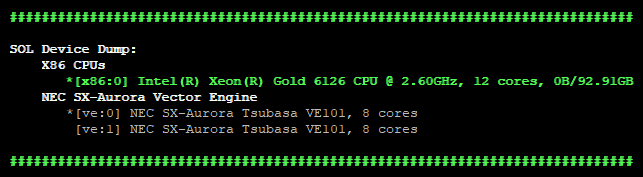 Green: device is initialized (has been used for computations). Star: default device. Green: device is initialized (has been used for computations). Star: default device. |
sol.plugins() |
Prints overview of loaded plugins. 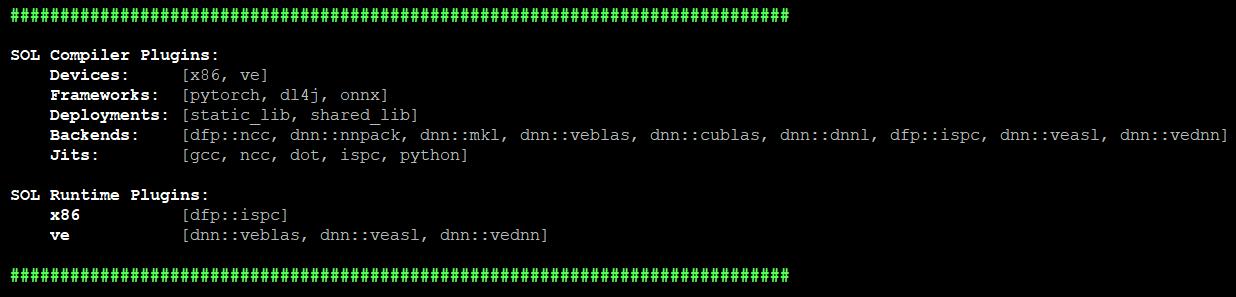 |
sol.seed(deviceType=None, deviceIdx=None) |
Fetches the global seed (both == None), the device type’s seed or the seed of a specific device. |
sol.set_seed(seed, deviceType=None, deviceIdx=None) |
Sets the seed. |
sol.seeds() |
Prints seed overview: 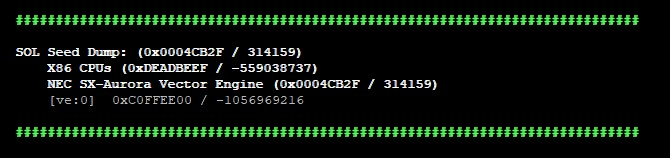 |
For offloading the data needs to be on the host system, otherwise implicit copy is not possible!