Frameworks
Running SOL in a framework is the easiest operation mode, as SOL takes care of most parameters, options, etc. automatically. In principle you just need to load SOL and run the sol.optimize(model, args, kwargs={}, *, framwork=None, vdims=None, **fwargs) function on your target model.
See subchapters for details on the different frameworks and example codes.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| model | Your model you want to optimize using SOL. |
| args | Either a list or tuple of framework tensors or other inputs. |
| kwargs | A dictionary of named arguments. |
| framework | A framework in which the returned model shall be executed. By default the same as the input model. |
| vdims | A list or tuple containing the value you want to assign to the variable dimension. Valid values are positive integers or None for variable values. |
| determinism | A set, list or tuple sol.Determinism enum items. Click here for more details. |
| fwargs | A dictionary containing framework specific flags. See corresponding framework for available flags. |
Generic Model Functions
SOL models are implemented using the framework’s own model structure, so they provide the same functionality as the framework’s models, except that SOL models always assume, that training = False for inference and training = True for training runs. Additionally they support following functions:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
model.__sol__.network |
Unique hash of the network. |
model.__sol__.free_ctxs() |
Forces to free all SOL contexts of this network on all devices. |
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
sol.__version__ |
SOL version string |
sol.cache.clear() |
Clears SOL’s build cache, to enforce rebuild of models. |
sol.check_version() |
Checks if a new version of SOL is available |
sol.config.print() |
Prints all config options and their current values |
sol.config["..."] = ... |
Sets config options |
sol.deploy(...) |
Details here |
sol.device.disable(device) |
See sol.device.enable(device) |
sol.device.enable(device) |
Enables code generation for the specified device. By default all available devices will be build. Device needs to be sol.device.[x86, nvidia, ve] |
sol.device.set(device, deviceIdx, *, bind_thread=False) |
Forces SOL to run everything on the given device. If the data is not located on the target device, it will be explicitly copied between the host and the device. By default the device is bound to all threads of the process. Using bind_thread=True you can bind the device only to the current thread. The thread’s setting is always preceeded over the process setting. |
sol.devices() |
Prints overview of available devices. 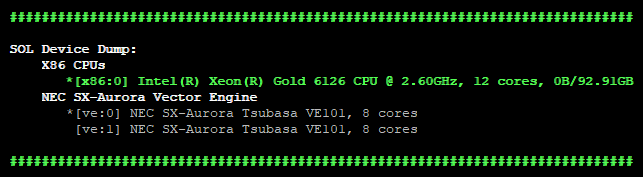 Green: device is initialized (has been used for computations). Star: default device. Green: device is initialized (has been used for computations). Star: default device. |
sol.env() |
Prints Env Vars + values used by SOL. 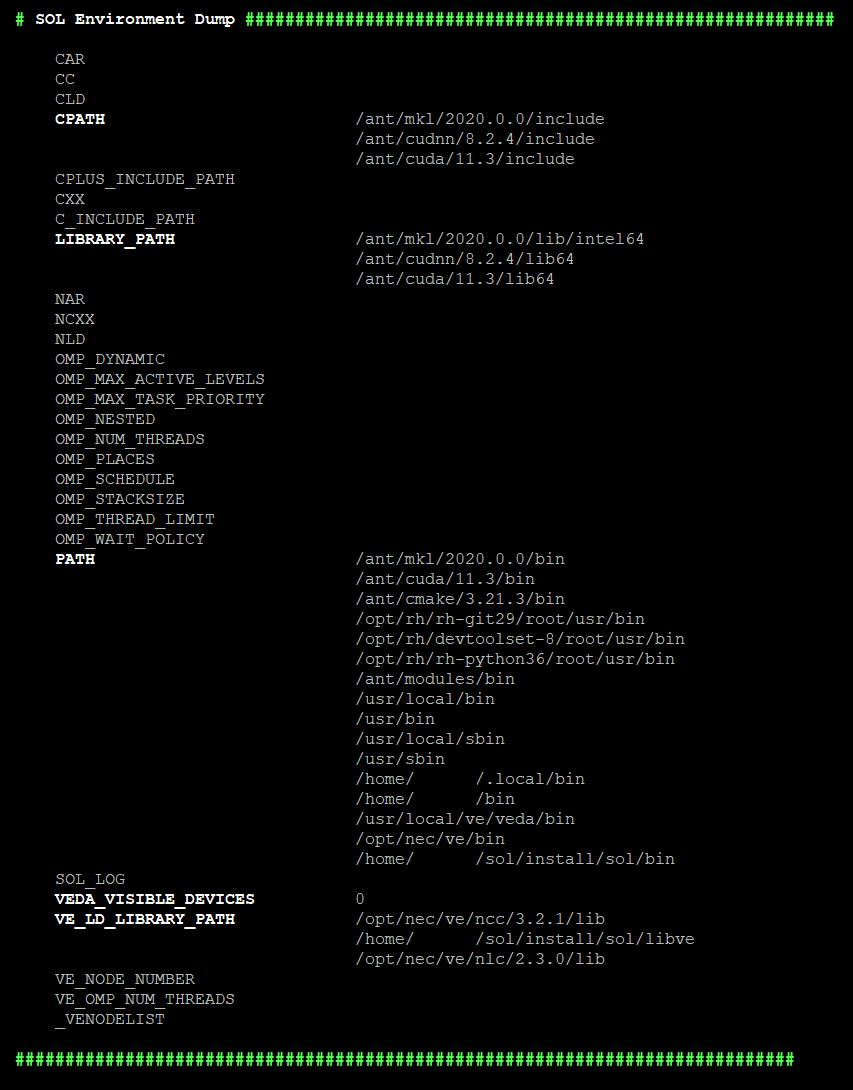 |
sol.optimize(...) |
Details here |
sol.plugins() |
Prints overview of loaded plugins. 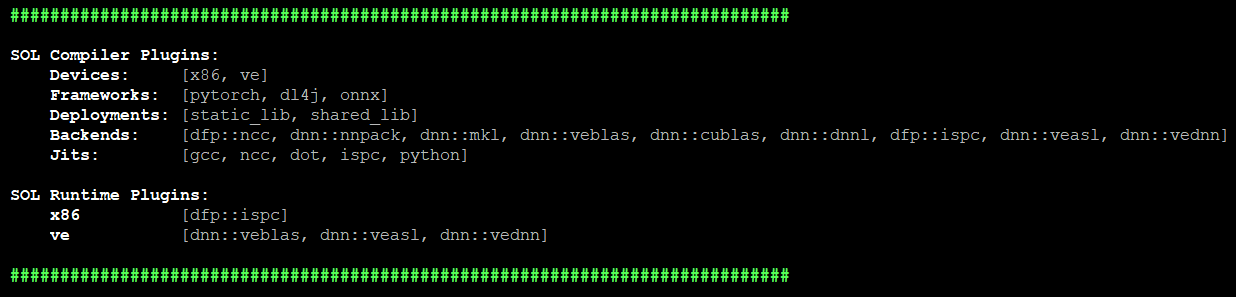 |
sol.seed(deviceType=None, deviceIdx=None) |
Fetches the global seed (both == None), the device type’s seed or the seed of a specific device. |
sol.seeds() |
Prints seed overview: 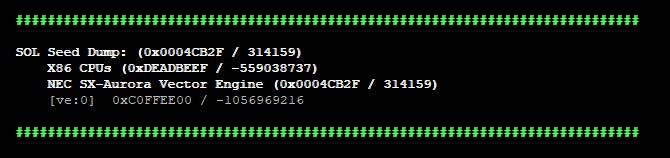 |
sol.set_seed(seed, deviceType=None, deviceIdx=None) |
Sets the seed. |
sol.versions() |
Prints versions of used compiler and libraries. 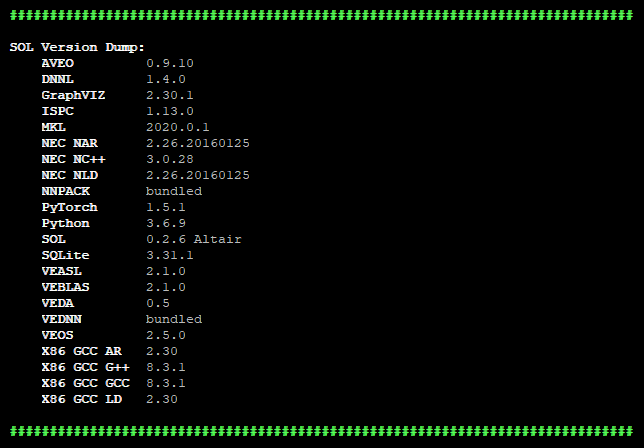 |
For offloading the data needs to be on the host system, otherwise implicit copy is not possible!